A respirator is a personal protective device used for protection against inhalation of contaminated air. It depends on the respirator which particles, gases and vapors it protects against. It depends, among other things, on the filter type the respirator is equipped with. Therefore, be sure that it meets the requirements of the work task and the working environment when you buy a respirator. Working with a respirator is stressful. It is particularly stressful to work with filtering respirators, which strain breathing. Limitations have therefore been set for the time of use - Observe this, as your circulation (heart) in particular is stressed and can be damaged by prolonged use.
There are three main types of respirators:
- Filtering respirator with breathing resistance
- Respirator with turbo filter without breathing resistance
- Air-supplied respirator
Before you get started, it is a good idea to have found data sheets for the products to be worked with. Without a data sheet, it is difficult to find the right protection.
CHOOSE THE RIGHT RESPIRATORY PROTECTION
STEP 1 – Which mask?
There are different mask types. Some are suitable for long-term use, while others are discarded after use. In addition, there is a difference in how many hours the different mask types may be used. Some may only be used for 3 hours a day, while others may be used for an entire working day. The table below gives a quick overview of what the different mask types can do.
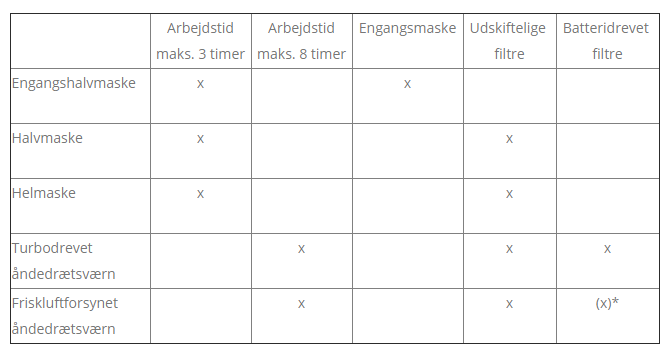
* Fresh air-supplied respirators must use a power source
Filtering disposable mask:
This type of mask is ONLY usable if you work in dust or particles. The mask therefore does NOT protect against chemicals and vapours. The mask is a disposable mask and must be discarded after the end of the working day. If there is dust and dirt on the inside, it must be discarded immediately. The mask is available both with and without a valve.
Working hours: 3 hours a day. (per 24 hours, not per working day!)
The mask is available in 2 versions; P2 and P3. (P1 discontinued)
P2: Can be used against harmful and toxic dust, but not against radioactive dust, bacteria and viruses. These filters protect against solid particles alone or against both solid particles and liquid aerosols. If the filter is tested according to EN149:2001, the filter protects against both solid particles and liquid aerosols.
P3: Has the greatest excretion rate and protects like class P2 and against radioactive dust, bacteria and viruses. The filter is normally for use against both solid particles and liquid aerosols.
If the filter is tested according to EN149:2001, the filter protects against both solid particles and liquid aerosols.
Half mask:
The most used mask is a half mask. The mask has replaceable filters, and can therefore be used for virtually all types of work. The mask is personal, so you cannot share the mask with friends or colleagues, as the mask molds to your face to optimize tightness. It is not recommended that men with large beards use this type of mask, as it will make the mask leaky. If you have a lot of beard, a full face mask is recommended.
The mask can be reused and requires minimal maintenance. It is recommended to replace the sealing edge at least once a year.
The filters must be replaced as needed, or after 3 weeks after unpacking the packaging.
Working hours: 3 hours a day (per 24 hours, not per working day!)
Some masks are available in different sizes. The most common size is medium (M).
Full mask:
A full face mask is widely used. The mask covers the entire face, so it is not necessary to use safety glasses.
The mask is a personal protective device, so you cannot share the mask with friends or colleagues, as the mask molds to your
face. Men with large beard growth must be aware that the rubber edge must close completely to the skin. It may therefore be necessary to trim the beard. The mask can be reused and requires minimal maintenance. It is recommended to replace the sealing edge at least once a year. The filters must be replaced as needed, or after 3 weeks after unpacking the packaging.
Working hours: 3 hours a day (per 24 hours, not per working day!)
Turbo Powered Respirator:
You must use a turbo powered respirator if you have to work with a mask for more than 3 hours a day. With such a set, you have to work a full working day with a mask on (8 hours).
The turbo unit draws fresh air into the mask, so that the lungs are not strained in the same way as when you have to draw the air in through the filters yourself. The turbo unit is battery powered and lasts approx. 8 hours, after which it must be charged.
Appropriate filters must be attached to the turbo unit, which sort out what you do not want to inhale.
The mask, like all other masks, is personal, which means that you cannot share a mask. The turbo unit, on the other hand, can easily be split and connected to various approved mask types that are suitable for the turbo unit. The mask can be reused and requires minimal maintenance. It is recommended to replace the sealing edge at least once a year.
The filters must be replaced as needed, or after 3 weeks after unpacking the packaging.
Working hours: 8 hours per Day.
Fresh air-supplied respirator:
If you work in a room where there is no oxygen, or where the air is so polluted that it cannot be separated using a normal filter, this type can be used. With this type of respirator, you have an air source standing outside in fresh and clean air, which supplies the workers with clean air via long hoses. The workers wear a full mask to which a hose is connected.
Working hours: 8 hours per Day.
Get specific advice and help for the most complete and effective solution by calling customer service on Tel: +45 71 99 32 60
STEP 2 – Choose the right filter:
Once you have found the type of mask that meets your needs, you must find the right filter protection that protects against the inhalation of toxic and harmful substances.
STEP 2.1 - Find the right filter for your mask:
First of all, you must find the filter type that fits the mask you have chosen. At Sikkerhedsgiganten.dk, we have made it easier for you. Under all masks you will find "related products", which show all the filters that match your mask.
STEP 2.2 - Knowledge of the filters:
Now you have found the filters that fit your mask, then we need to find the filter type(s) that will protect you. All the protection classes are marked with colors and letters. Some are completely brown, others are green, and some have multiple colors. The meanings of the colors and letters are described below. If a filter has several colors, it is because it is a "combi filter" that protects you against several things at once.
Gas filters:
A - Brown: Against organic vapors from substances with a boiling point above 65 degrees
AX - Brown: Against organic vapors from substances with a boiling point of 65 degrees or below
A+ - Brown/olive green: Against organic vapors from substances with a boiling point above 65 degrees
B - Grey: Against inorganic gases and vapours
E - Yellow: Against acid gases and vapours
K - Green: Against ammonia and other gases
HgP3 - Red/white: Against vapors of metallic mercury
NO-P3 - Blue/white: Against nitrous gases and particles
SX - Violet: Against special substances
CoP3 - Black/white: Against carbon monoxide and particles
The gas filters often classified with e.g. A1 or A2, the number is an expression of the capacity. 1 is the lowest, with 2 being the best. When it says "best", it is not an expression that 1 is of poorer quality, it just does not last as long as a filter that is classified with a 2 number. If you are in doubt about what capacity your filter should have, go for capacity 2.
Particulate filters:
These filters have no color code, but will typically be white if they are found in combination with other filter protections, or they are characterized only by their "P" (particle) and their number. The numbers go from 1-3. But since P1 is about to expire, we do not take it into account in the guide.
P2 - Can be used against harmful and toxic dust, but not against radioactive dust, bacteria and viruses. These filters can protect against solid particles alone or against both solid particles and liquid aerosols.
P3 - Has the greatest excretion rate and protects like class P2 as well as against radioactive dust, bacteria and viruses. The filter is normally for use against both solid particles and liquid aerosols.
STEP 2.3 - Learn to read the data sheet
Now you have become a little wiser about the importance of filters, now you have to learn how to decide which type of protection to choose.
Now you need to use your product data sheet(s) on the product(s) you need to protect against. You can always obtain these data sheets by contacting your chemical dealer, they must be able to hand them over to you in Danish.
The information about the use of personal protective equipment can always be found under point 8 in the data sheet.
Below is a data sheet for a chlorine cleaning product.
If we look at the breathing part, the data sheet recommends using a B/P2 filter protection. If we go up in STEP 2.1, we can see that B filtered is this:
B - Grey: Against inorganic gases and vapours
The data sheet has even written the color code to make it easier.
In addition, we must use a P2 protection, which protects against particles. Depending on the type of mask you have chosen, there are different options. Some make a combination, while other brands require you to put two filters together.
STEP 2.4 - Which filter
If we look at this Pro2000 filter from Scott, for example, we can see that they have made a combination of B2 and P3 filter.
The number 2 in B2 is an expression of the capacity of the filter. The data sheet recommends a capacity of 1, but nothing happens by increasing it
a better capacity, but NEVER vice versa!
If a brand does not offer a combination of B and P, a separate P filter can be purchased to click on top of the B filter. This can both be called a P-filter or a pre-filter, which often requires a pre-filter holder in order to be put on the gas filter.
Another challenge may be that the brand does not offer a separate B filter at all. This challenge is encountered often. Here it may be necessary to buy a combi-filter to achieve its B protection.
See e.g. this filter Sundström filter:
Sundström does not make a separate B filter, it is therefore necessary to take a combi filter like this.
This filter is an: A1B1E1K1 filter, that is to say it protects against several gases and vapours. With this filter, you are therefore protected with B1, as the data sheet above prescribes.
It is never wrong to be protected for more than the data sheet prescribes, but it must never be the other way around! As long as B1 (or B2) is included in the combi-filter, you can use this filter for excess chlorine cleaning product.
BUT the above filter does not have P2 protection. If you do not use a P protection, as the data sheet prescribes, all the particles in the air will not be separated in the filter and will therefore end up in your lungs.
Therefore, you must buy a P filter and combine it with this combi-filter.
With this P3 filter and the combi filter, you are fully covered when you use excess chlorine product. The filters are made to click together and it cannot be done wrong. But always remember that the P filter must be on the outermost part.
KNOWLEDGE AND CARE OF MASK AND FILTERS
You extend the life of your mask and filters if you take good care of them. Below are the most basic things you can do to extend the life of your mask.
Cleaning:
Your mask will get dirty with use, this especially applies to the sealing edge, which makes the mask close to the face. This is because the skin secretes fat and dead skin cells. If the edge is not wiped off after use, the mask may have difficulty closing completely, which means that dirt, grime and gases may enter the wrong side of the mask. Therefore, wipe off the mask every time you have used it. This is done easily with the special cleaning wipes that degrease and disinfect the mask.
Storage:
Proper storage extends the life of your mask and filters. You protect them best by storing them in the special storage boxes for masks, which are both dust, air and waterproof. It is very important that the mask is stored in a clean and airtight container so that it does not become contaminated inside. The same applies to the filters, as the oxygen "uses" the filters when they are outside.
Remember to clean the mask before placing it in the storage box.
Replacing filters:
It can be difficult to know when the filters need to be replaced, and there is no concrete guide for this either. In this section you will find some rules that you can follow.
Particulate filters (P2/P3) have no lifetime in contrast to gas filters. The longer you use your P filter, the safer and tighter it becomes, as the air particles "stop" the filter and prevent more particles from entering. BUT you must pay attention to your breathing. The more clogged the particle filter is, the more strenuous it becomes to pull the weight through the filter. If you find that breathing becomes more strenuous, it is time to change your particle filter.
As a starting point, gas filters must be replaced 3 weeks after they have been taken out of the packaging. This applies regardless of whether you have used the filter during that time or not. However, it may be necessary to change filters earlier, as the active substance will be broken down by the vapors or gases it is exposed to, thereby losing its protective effect. It depends on how powerful the disposal is and how much air the user uses.
Sometimes you can use a filter for several weeks, other times only for 1-2 days. A rule of thumb is to take your time during use, and as soon as you can taste/smell/feel the product you are working with through the mask, you must change filters. If you then subtract 3 hours, you have the time interval when you have to replace the filters.